Criminal Felony Procedure
One of the most frequently asked questions that our office receives is how a felony case proceeds through the Criminal Justice System for prosecution. Below is a basic flow chart to help you understand the mechanics of a Criminal Felony Prosecution. Below the flow chart is a list of commonly used terms in the Criminal Justice System and their definitions.
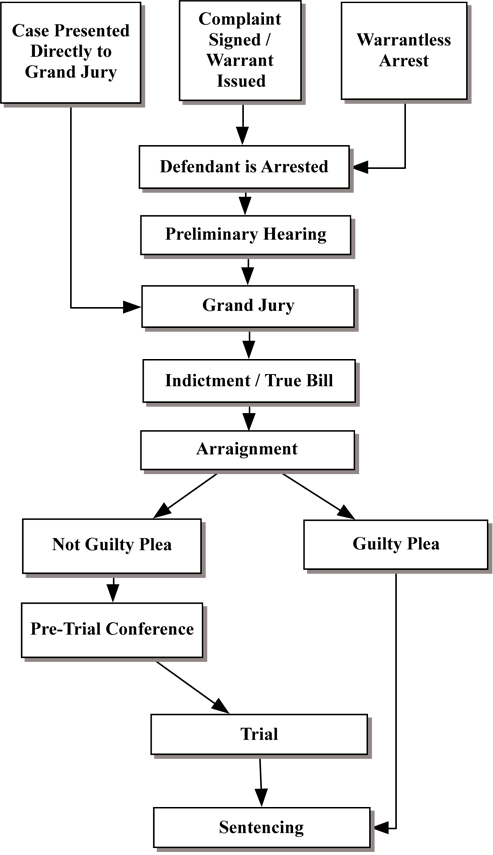
Terms Commonly Used in the Criminal Justice System
- Arraignment:
- The formal hearing where the accused enters a plea of guilty or not guilty.
- Bench Trial:
- A trial in which the Judge is the finder of fact, not a jury.
- Bound Over:
- When the case is transferred from the District Court to the Grand Jury.
- Bond:
- The mechanism that allows a defendant out of jail pending his/her trial.
- Bond Revocation:
- If the defendant is accused of violating any conditions placed on the bond order that allows the defendant out of jail, a hearing takes place to determine the consequences (usually return to jail).
- Contempt of Court:
- When a person violates a civil order of the court.
- District Attorney’s Office:
- The office that prosecutes all felony cases and county misdemeanors on behalf of the State of Alabama.
- Defendant:
- The person who is accused of a criminal act.
- Defense Attorney:
- The attorney for the person accused of a crime.
- Discovery:
- The term used to describe the official procedure for a defendant or their attorney to obtain legal information about the State’s case.
- Deferred Prosecution Programs:
- Programs for defendants who are first time offenders for certain crimes. Successful completion would likely result in the dismissal of criminal charges.
- Grand Jury:
- A jury of 18 people who hear evidence presented by the District Attorney’s Office regarding felony charges. The charges are drawn on a document called an indictment. It is the legal mechanism used to determine if there is enough probable cause to move a felony case from District Court to Circuit Court for a trial.
- Habitual Offender:
- A person who has a recidivist record will be identified as habitual offender and may face enhanced punishment.
- Indictment:
- A formal charging document that is produced by the District Attorney’s Office through the Grand Jury and is submitted to the Clerk of Court as the official charge(s) against a defendant. These are the charges that the State is required to prove in a trial.
- Jury Trial:
- A trial in which a jury of peers is the finder of fact.
- Motions:
- Procedures in which the prosecutor and defense attorney argue in front of a Judge about what specifically is and is not allowed in a pending trial.
- No Bill:
- The term is used when a Grand Jury does not find sufficient evidence to proceed with charges against a defendant.
- Nolle Pros:
- The procedure in which the prosecutor may dismiss a case after charges have been filed with the Court.
- Preliminary Hearing:
- A hearing in front of a District Court Judge to gain more information from the parties involved as it relates to probable cause.
- Probable Cause:
- The measure of standard required before a District Court Judge can bind a case over to Grand Jury or issue a warrant.
- Probation:
- An alternative to jail that often includes various conditions that the defendant must comply. Often times involving counseling and/or treatment.
- Probation Revocation:
- A hearing to determine if the defendant has violated conditions of his/her probation and subsequent consequences.
- Prosecutor:
- The attorney for the State of Alabama.
- Reasonable Doubt:
- The level of proof required by the State to prove the charges at trial.
- Restitution:
- The amount of money the Judge orders the defendant to pay at sentencing to reimburse a victim for out of pocket expenses.
- True Bill:
- The term is used when a Grand Jury finds sufficient evidence to proceed with charges against a defendant.
- Victim Compensation:
- A State of Alabama program which provides financial support for victims of crime for out of pocket expenses related to a crime. Types of expenses can include: medical, funeral, mental health, lost wages, and loss of support.







